Performance and Recovery Optimization
With our innovative approach to recovery, we provide cutting edge-technology and protocols that enhance performance and well-being. Recover from stress, injury, burnout. Replenish routinely.
Effective Recovery to Enhance Your Performance and Flow
Gain strength without lifting weights? Yes. Reset and balance your body and neurochemistry. Unlock Neuromuscular and Biostimulation that will leave you feeling revived and refreshed – guaranteed.
Stress + Recovery = Adaptation (Better Performance).
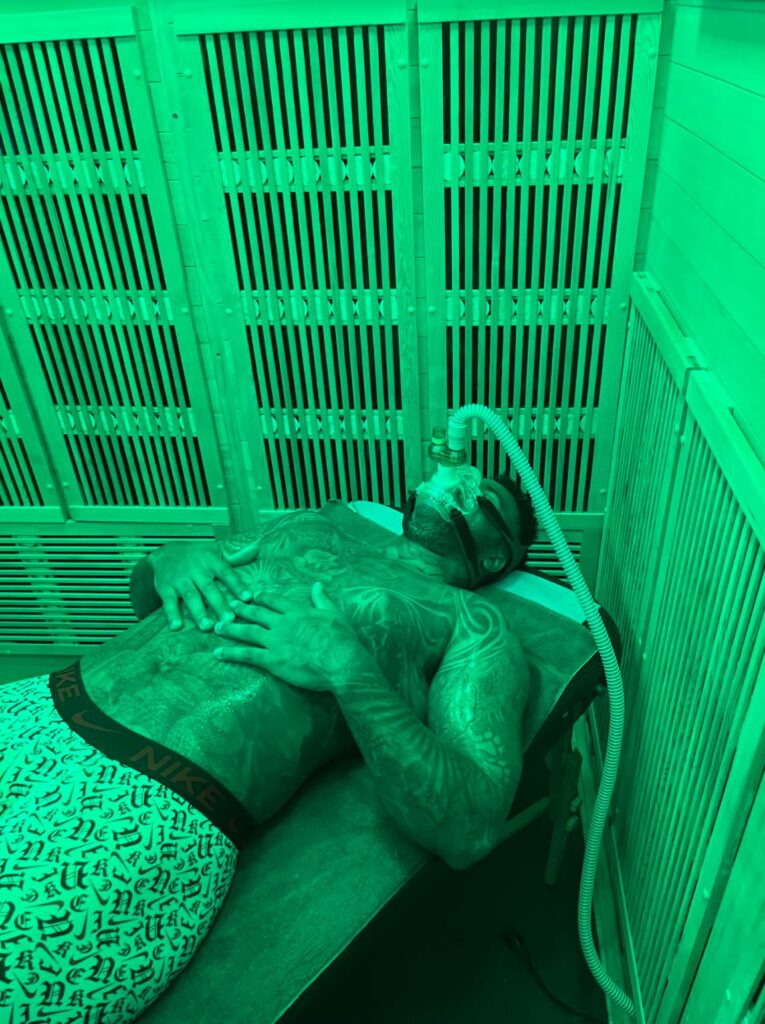



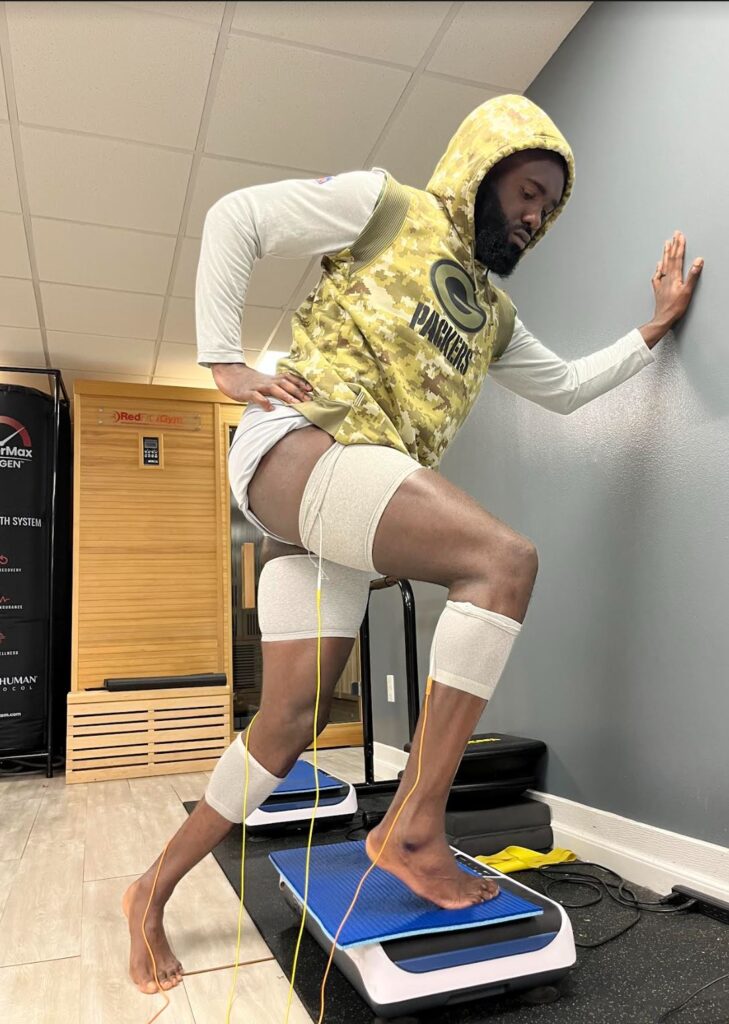


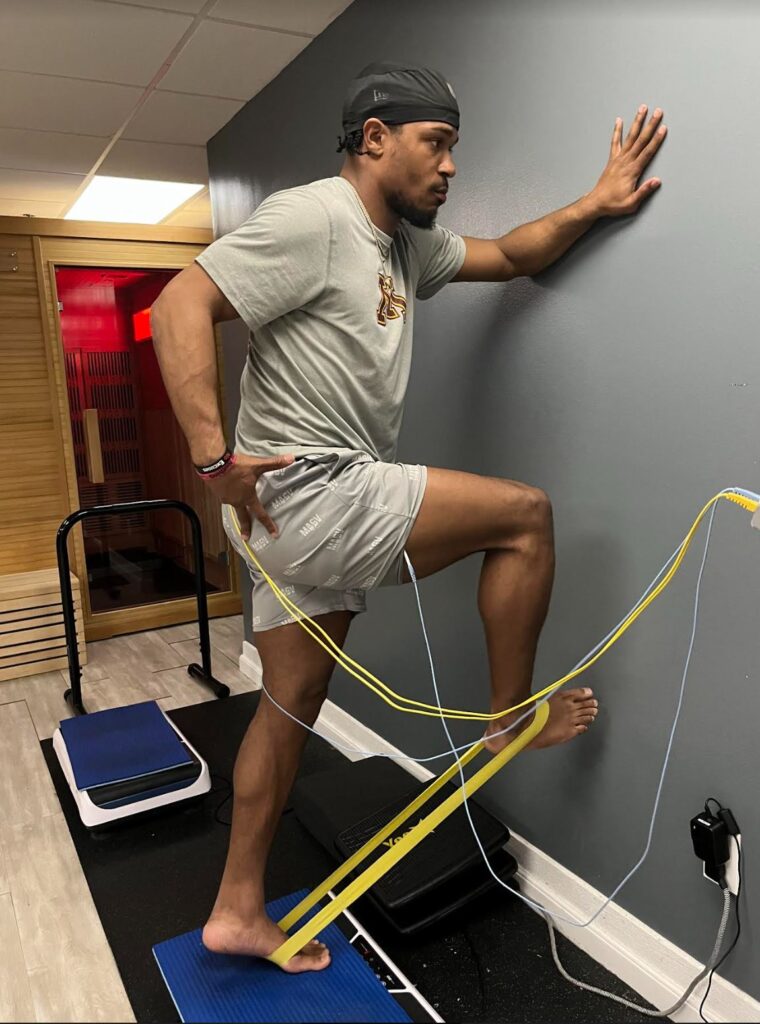

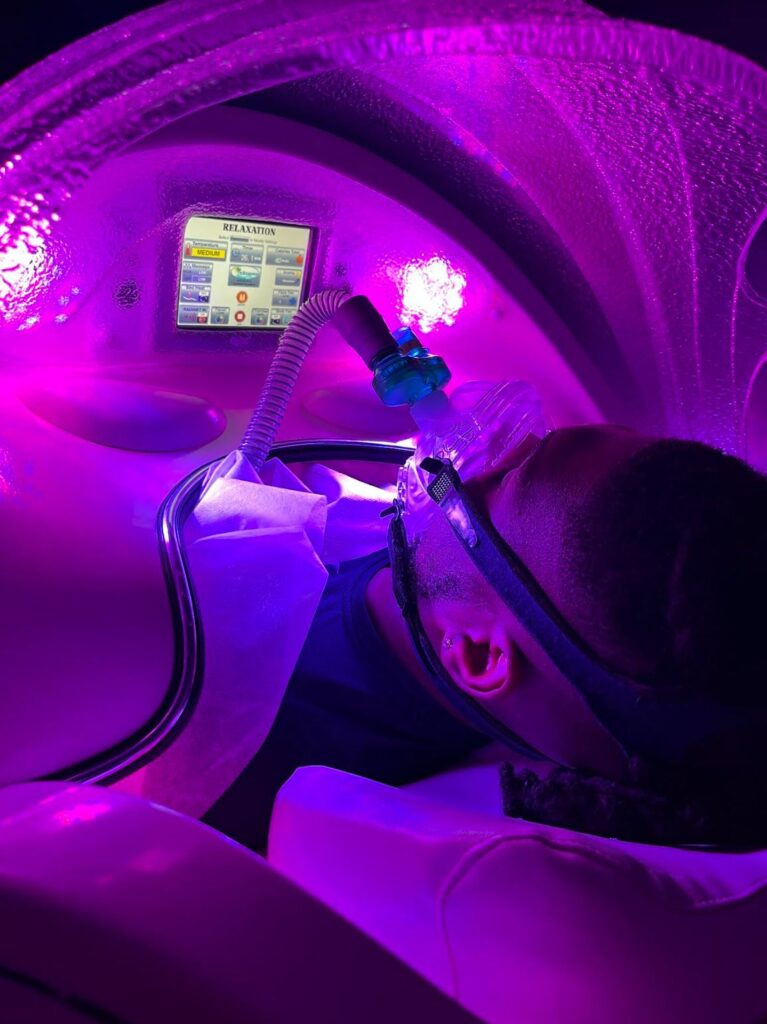

I was killing myself in the gym, overlifting, overstretching and stifling my performance. After just two weeks of torque and ground training in the saunas, my ankle pain vanished. I also sleep through the nights now and feel mentally and physically energized everyday. Thank you, Hyperthermix!
Frequently Asked Questions:
FAQ Center
Tier 1 and Tier 2 Sessions for Saunas, Cocoons and Vibration Plates are available for 20-30 minutes, each session.
Absolutely! For only $19 you can get complimentary BioScan and experience the toasty saunas, cocoons and vibration training for 30 minutes.
To get the full benefit of Hyperthermix Sauna and Vibrational Trainings, it is recommended that you do 2-3 sessions weekly. Find out what works best for you and your body.
The less the better, to allow maximum skin exposure for the release of sweat. This could be a bathing suit, shorts and a tank, etc. We also provide a towel wrap for each guest to use in the sauna if they wish. We recommend bringing a water bottle, water and restrooms are provided at the facility.
We advise you to use your time in the sauna as a moment to relax and meditate, allow the infrared heat to melt away any stress or fatigue you have. You may prefer reading a book, magazine, or even your phone or tablet into the sauna to pass the time. If you are feeling more active, you can walk on a treadmill, bike, row, or try out our groundwork, torque training, stretching, yoga, pilates, etc.
Infrared saunas work by using infrared heaters to emit infrared light experienced as radiant heat, which is absorbed by the surface of the skin. Unlike traditional saunas that heat the air around you, infrared saunas directly heat your body.
Here’s how they typically work:
Infrared Emitters: Infrared saunas contain several infrared emitters, usually made of ceramic or carbon materials. These emitters produce infrared radiation, which is a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than radio waves.
Penetration: The infrared radiation emitted by the heaters penetrates the skin and heats the body directly, rather than heating the air in the sauna chamber. This process raises the body’s core temperature, induces sweating, and promotes various health benefits.
Temperature Control: Infrared saunas allow users to control the temperature based on personal preference. Temperatures typically range between 100°F to 150°F (38°C to 65°C). Despite the lower air temperature compared to traditional saunas, users often feel as though they are experiencing a more intense heat due to the direct heating effect of the infrared radiation.
Sweating and Detoxification: The heat generated by the infrared radiation causes the body to sweat profusely. Sweating is the body’s natural way of detoxifying by eliminating toxins through the skin pores. Many proponents of infrared saunas believe that this detoxification process can help cleanse the body of impurities and promote overall health and well-being.
Health Benefits: Advocates of infrared saunas claim various health benefits, including improved circulation, relaxation, pain relief, weight loss, and skin purification. While some of these benefits are supported by anecdotal evidence and small-scale studies, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and effectiveness of infrared sauna therapy for different health conditions.
Overall, infrared saunas offer a different sauna experience compared to traditional saunas, primarily due to the way they heat the body directly with infrared radiation. However, individuals with certain medical conditions or concerns should consult with a healthcare professional before using an infrared sauna to ensure it is safe for them.
Neuromuscular stimulation, also known as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) or electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), is a therapeutic technique that uses electrical impulses to activate muscles, nerves, and related tissues. It is commonly used in rehabilitation, sports medicine, and fitness settings for various purposes, including muscle strengthening, pain management, and muscle re-education.
Here’s how neuromuscular stimulation typically works:
Electrodes Placement: Electrodes are placed on the skin over the target muscles or nerves. These electrodes are connected to a device that delivers electrical impulses.
Electrical Impulses: The device delivers controlled electrical impulses to the electrodes, which then stimulate the underlying muscles or nerves. The intensity, frequency, and duration of the electrical impulses can be adjusted based on the specific treatment goals and individual needs.
Muscle Contraction: The electrical impulses cause the muscles to contract involuntarily, mimicking the natural contractions that occur during physical activity. These contractions can help strengthen weak muscles, improve muscle tone, and prevent muscle atrophy, particularly in individuals who are unable to engage in voluntary exercise due to injury, illness, or other limitations.
Pain Management: Neuromuscular stimulation can also be used to relieve pain by stimulating the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural pain-relieving chemicals. Additionally, the muscle contractions induced by electrical stimulation can help reduce muscle spasms and tension, providing relief from musculoskeletal pain and discomfort.
Muscle Re-education: In rehabilitation settings, neuromuscular stimulation is often used to facilitate muscle re-education and improve movement patterns in individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries. By targeting specific muscle groups and guiding them through controlled contractions, neuromuscular stimulation can help restore normal muscle function and improve coordination and proprioception.
Performance Enhancement: In sports and fitness applications, neuromuscular stimulation is sometimes used to complement traditional training methods and enhance athletic performance. By selectively targeting muscle groups and eliciting strong, coordinated contractions, electrical stimulation can help athletes improve strength, power, and muscle endurance.
Overall, neuromuscular stimulation is a versatile therapeutic modality with various applications in rehabilitation, pain management, and performance enhancement. However, it’s essential to use this technique under the guidance of trained professionals to ensure safe and effective treatment outcomes.
Recovery optimization refers to the process of enhancing and maximizing the body’s ability to recover from physical exertion, stress, injury, or illness. It involves implementing strategies and interventions to promote faster and more effective recovery, allowing individuals to return to optimal function, performance, and overall well-being.
Here are some key components of recovery optimization:
Rest and Sleep: Adequate rest and quality sleep are essential for recovery. During sleep, the body undergoes repair and regeneration processes, including muscle growth, tissue repair, and hormone regulation. Prioritizing sufficient sleep and allowing for adequate rest between workouts or periods of intense activity is crucial for optimal recovery.
Nutrition: Proper nutrition plays a critical role in supporting recovery by providing essential nutrients, energy, and building blocks for tissue repair and growth. Consuming a balanced diet rich in protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals helps replenish glycogen stores, repair damaged tissues, and promote overall recovery.
Hydration: Staying hydrated is important for maintaining optimal physiological function and supporting recovery processes. Proper hydration helps regulate body temperature, facilitate nutrient transport, and remove metabolic waste products from tissues. Drinking an adequate amount of water and electrolytes before, during, and after physical activity is essential for promoting recovery.
Active Recovery: Engaging in light exercise or low-intensity activities, such as walking, cycling, or yoga, can help promote blood flow, reduce muscle soreness, and facilitate recovery. Active recovery sessions can help flush out metabolic byproducts, enhance nutrient delivery to muscles, and promote relaxation and recovery without causing additional stress to the body.
Recovery Modalities: Various recovery modalities and techniques, such as massage, foam rolling, stretching, contrast baths, cryotherapy, and compression therapy, can help alleviate muscle soreness, reduce inflammation, and accelerate recovery. These modalities work by promoting circulation, reducing muscle tension, and enhancing tissue repair and regeneration.
Stress Management: Managing stress is important for optimizing recovery, as chronic stress can negatively impact immune function, hormone balance, and overall well-being. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can help promote recovery by reducing stress levels and promoting a state of relaxation and recovery.
Individualization: It’s essential to tailor recovery strategies to individual needs, preferences, and goals. Factors such as age, fitness level, training intensity, injury history, and genetic predispositions can influence the effectiveness of different recovery strategies. Experimenting with different approaches and finding what works best for each individual is key to optimizing recovery.
By incorporating these principles into a comprehensive recovery plan, individuals can enhance their ability to recover effectively, minimize the risk of injury, and maintain optimal performance and well-being over the long term.
Phototherapy: Phototherapy involves the use of specific wavelengths of light to stimulate biological processes in the body. In a photothermic sauna, specialized lights, such as LEDs or near-infrared lights, may be installed within the sauna to emit therapeutic wavelengths of light. These lights could be strategically positioned to target different areas of the body.
Thermotherapy: Thermotherapy refers to the application of heat for therapeutic purposes. In a photothermic sauna, heat is typically generated using traditional sauna heaters, such as electric heaters or infrared heaters. The sauna chamber is heated to a comfortable temperature, which promotes relaxation, induces sweating, and helps alleviate muscle tension and stress.
Combination Therapy: By combining phototherapy with thermotherapy, a photothermic sauna aims to enhance the therapeutic effects of both modalities. The combination of light and heat can potentially amplify the benefits of each therapy, such as improving circulation, promoting detoxification, reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and enhancing overall well-being.
Health Benefits: Advocates of photothermic saunas claim various health benefits, including improved skin health, enhanced detoxification, increased relaxation, and reduced muscle soreness.
Light Therapy Integration: In a photonic sauna, specialized lighting systems are likely incorporated to emit specific wavelengths of light, such as red, near-infrared, or full-spectrum light. These wavelengths of light can have various therapeutic effects on the body, including promoting relaxation, improving circulation, supporting cellular repair and regeneration, and reducing inflammation.
Infrared Technology: Since infrared saunas have gained popularity for their therapeutic benefits, a photonic sauna may also utilize infrared technology. Infrared saunas emit infrared light waves that penetrate the skin and heat the body directly, resulting in a range of health benefits such as detoxification, pain relief, relaxation, and improved skin health.
Phototherapy: Photonic saunas may incorporate phototherapy techniques, which involve exposing the body to specific wavelengths of light to stimulate biochemical processes in the body. For example, red and near-infrared light therapy has been studied for its potential to enhance mitochondrial function, increase ATP production, reduce oxidative stress, and promote tissue repair.
Therapeutic Benefits: By combining the benefits of light therapy with the heat of a sauna environment, a photonic sauna aims to provide a comprehensive wellness experience. Users may experience relaxation, stress relief, improved sleep quality, muscle recovery, and enhanced overall well-being.

